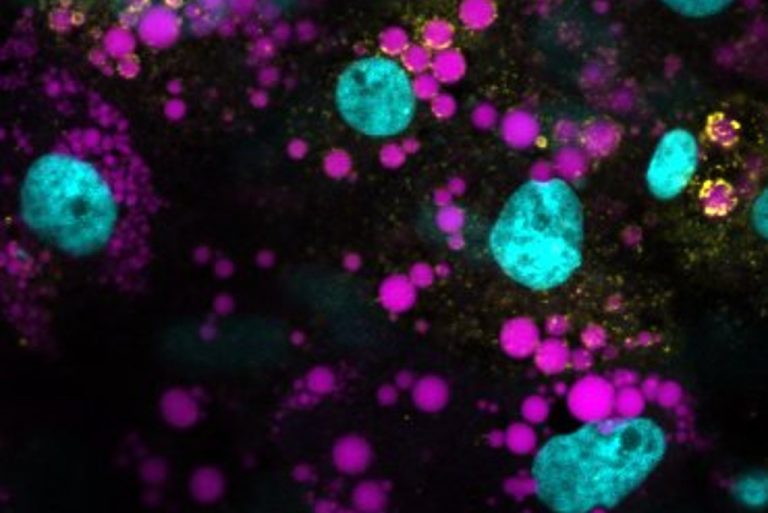
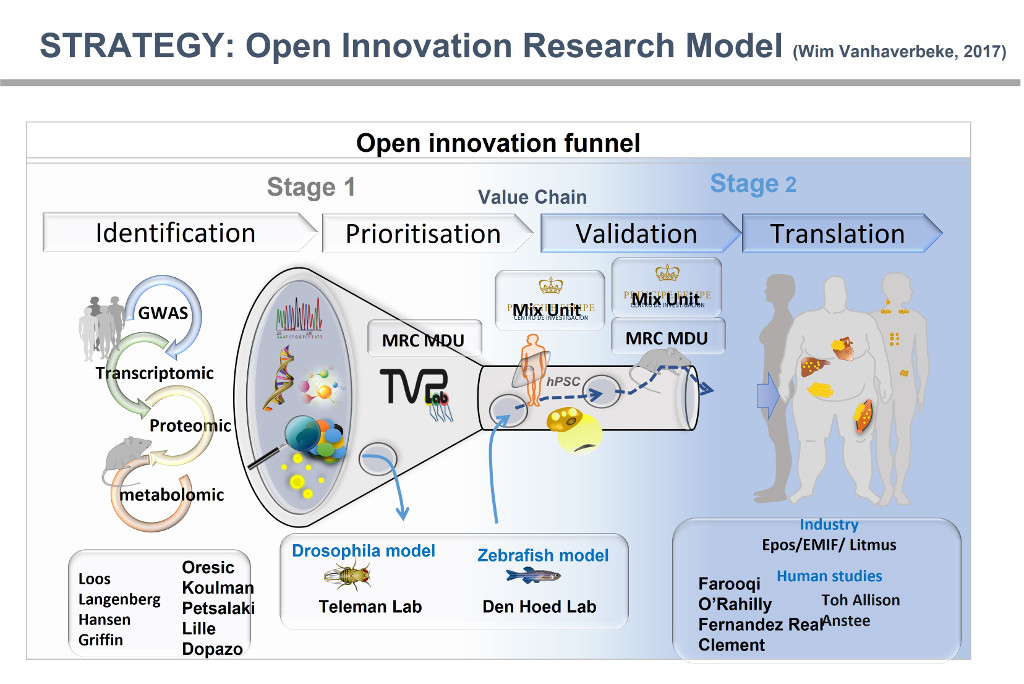
The TVPLab
Our research program explores the molecular mechanisms involved in controlling energy expenditure, fat deposition and the mechanisms controlling the partition of energy towards oxidation or storage. are interested in the following interrelated questions:
- How the expansion of adipose tissue relates to the development of the Metabolic Syndrome?
- How lipotoxicity and/or changes in adipokines secreted by adipose tissue affect insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle, heart, liver, brain, beta cells and macrophages?
- Whether modifications in adipogenesis and remodeling of adipose tissue may be good strategies to ameliorate the metabolic effects of obesity?
- Elucidation of the molecular mechanisms that control energy expenditure and brown fat activation.
- Investigating how mechanisms modulating the partitioning of nutrients towards fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle and away from storage in adipose tissue may prevent the devastating metabolic effects of obesity.
To address these challenges is a daunting task that requires the modulation of highly integrated and complex mechanisms of energy homeostasis designed to energy balance. According to this integrated concept of energy homeostasis, our laboratory uses an Integrated Physiology approach that relies significantly upon the generation and detailed in vivo phenotyping of genetically modified organisms. Following a Systems Biology approach, we integrate transcriptomic and lipidomic analysis using bioinformatics to identify organ-specific lipid metabolic networks relevant to insulin resistance and metabolic disease.
Presentation
Get to know us better
Research Staff
The people who make it all possible
Antonio Vidal Puig
avidal-puig@cipf.es
Stefania Carobbio
scarobbio@cipf.es
Publications
Our scientific contributions
SREBP1-induced fatty acid synthesis depletes macrophages antioxidant defences to promote their alternative activation.
Bidault G, Virtue S, Petkevicius K, Jolin HE, Dugourd A, Guénantin AC, Leggat J, Mahler-Araujo B, Lam BYH, Ma MK, Dale M, Carobbio S, Kaser A, Fallon PG, Saez-Rodriguez J, McKenzie ANJ and Vidal-Puig A
Nature Metabolism, 2021 Sep, DOI: 10.1038/s42255-021-00440-5, Vol. 3, pag. 1150-1162
Allostatic hypermetabolic response in PGC1a/ß heterozygote mouse despite mitochondrial defects.
Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Lelliot CJ, Campbell M, Peddinti G, Martinez-Uña M, Ingvorsen C, Dias AR, Relat J, Mora S, Hyötyläinen T, Zorzano A, Orešic M, Bjursell M, Bohlooly-Y M, Lindén D and Vidal-Puig A
FASEB JOURNAL, 2021 Sep, DOI: 10.1096/fj.202100262RR, Vol. 35, pag.
Unraveling the Developmental Roadmap toward Human Brown Adipose Tissue
S. CAROBBIO, A. GUENANTIN, M. BAHRI, S. RODRIGUEZ-FDEZ, F. HONIG, I. KAMZOLAS, I. SAMUELSON, K. LONG, S. AWAD, D. LUKOVIC, S. ERCEG, A. BASSETT, S. MENDJAN, L. VALLIER, B. ROSEN, D. CHIARUGI and A. VIDAL-PUIG
Stem Cell Reports, 2021 Mar, DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.013, Vol. 16, pag. 641-655
Bone morphogenetic protein 8B promotes the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Vacca M, Leslie J, Virtue S, Lam BYH, Govaere O, Tiniakos D, Snow S, Davies S, Petkevicius K, Tong Z, Peirce V, Nielsen MJ, Ament Z, Li W, Kostrzewski T, Leeming DJ, Ratziu V, Allison MED, Anstee QM, Griffin JL, Oakley F and Vidal-Puig A
Nature Metabolism, 2020 Jun, DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-0214-9, Vol. 2, pag. 514-531
Adipocyte-secreted BMP8b mediates adrenergic-induced remodeling of the neuro-vascular network in adipose tissue.
Pellegrinelli V, Peirce VJ, Howard L, Virtue S, Türei D, Senzacqua M, Frontini A, Dalley JW, Horton AR, Bidault G, Severi I, Whittle A, Rahmouni K, Saez-Rodriguez J, Cinti S, Davies AM and Vidal-Puig A
Nature Communications, 2018 Nov, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07453-x, Vol. 9, pag. 4974-4974
FUNDING
Thank you for supporting us